Hyaluronic acid injections are gel or jelly-like substances that are administered into an affected knee in order to treat pain in the joint caused by osteoarthritis (OA). This therapy is initiated when conservative management via the use of oral pain relievers and other conservative measures are ineffective.
Hyaluronic acid works as a shock absorber and lubricant and is similar to the synovial fluid found in the knees which helps these joints function properly.
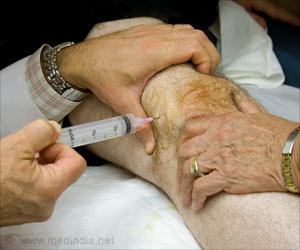
This medication is administered by a trained medical professional and a series of shots will be given one week apart for a total of three or four injections.
Factors to Consider Before Use
In order to use such a product to help reduce pain in the knees, one has to weigh out the benefits versus any possible risks the medication may have. Factors that need to be considered include:
- Allergies – patients known with any food allergies should inform their doctor before having hyaluronic acid administered into the knee. Of course, if there has been an allergic reaction to this medicine, or any other similar ones, then the patient should not be prescribed the product.
- Drug interactions – if any other prescription or non-prescription medications are being used by a patient, then the prescribing doctor should be notified of these in order to make the appropriate dose adjustments for the knee-gel injection.
- Other medical issues – problems such as being allergic to bacterial proteins or preparations containing hyaluronate, knee joint or overlying skin infections where the injection is to be administered, and too much fluid in the knee should be resolved before hyaluronic injections are administered in the joints.
Precautions
After the hyaluronic acid is administered into the knee joint, the doctor who gave the medication will check how the patient progresses. This allows the medical professional to assess if the medication is working properly and to decide whether to carry on with the treatment or not.
For the medication to work effectively, certain precautions need to be practiced by the patient and these include:
- Not straining the knee for two days after the medication is administered. Activities such as tennis, soccer, jogging, heavy lifting, and standing for a long period of time should be avoided.
- Some swelling or pain may be present after the medication is administered but if the symptoms are persistent or worsen then the patient should contact the doctor who performed the procedure.
- Avoid using disinfectants containing quaternary ammonium salts as these may inhibit the action of the hyaluronic acid.
Efficacy
Hyaluronic acid injections into the knee joints are safe and effective to the point that the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO) recommends intra-articular hyaluronic acid for the management of knee osteoarthritis in patients who remain severely symptomatic despite the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) also recommend hyaluronic acid injections for both pain reduction and joint functional improvement.
Both the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and ESCEO recommend the intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid in patients whose symptoms persist despite prior treatments.
